Natural, healthy and versatile
Gelatin is a natural and healthy food that can look back on a long tradition. Due to its versatile properties, the pure protein offers many benefits and plays an important role in today’s food industry. Gelatin can be used to gel, thicken, stabilize, emulsify and to give a creamy consistency. But that is not all: the all-rounder is used in various economic sectors and for a wide range of products. Gelatin is especially indispensable in the pharmaceutical and photo industries.
Protein, mineral salts and water
Gelatin is a pure, natural protein made from animal raw materials that contain collagen. It consists of 84 to 90 per cent protein and 2 per cent mineral salts, with water making up the rest. Gelatin is classified as a foodstuff and, is not a food additive with an E number. As a natural food, meeting ISO standards, gelatin fulfils therefore, among other reasons, the requirements of the clean label products, the demand for which is steadily growing. The use of artificial or modified additives, which need to be labelled with an E number, are avoided as much as possible in the production of food. Gelatin contains neither preservatives nor other additives and is free of fat, cholesterol and uric acid compounds.

Of great value for the organism
Without protein, there would be no human life. Over longer periods of time, the human metabolism can replace some nutrients, such as carbohydrates. Protein, however, is needed by the human body. Interestingly the human body, like other mammals, consists of approx. 30 percent collagen if water and blood is deducted. Gelatin is pure collagen and is therefore the ideal fit for the human body.
Versatile in use
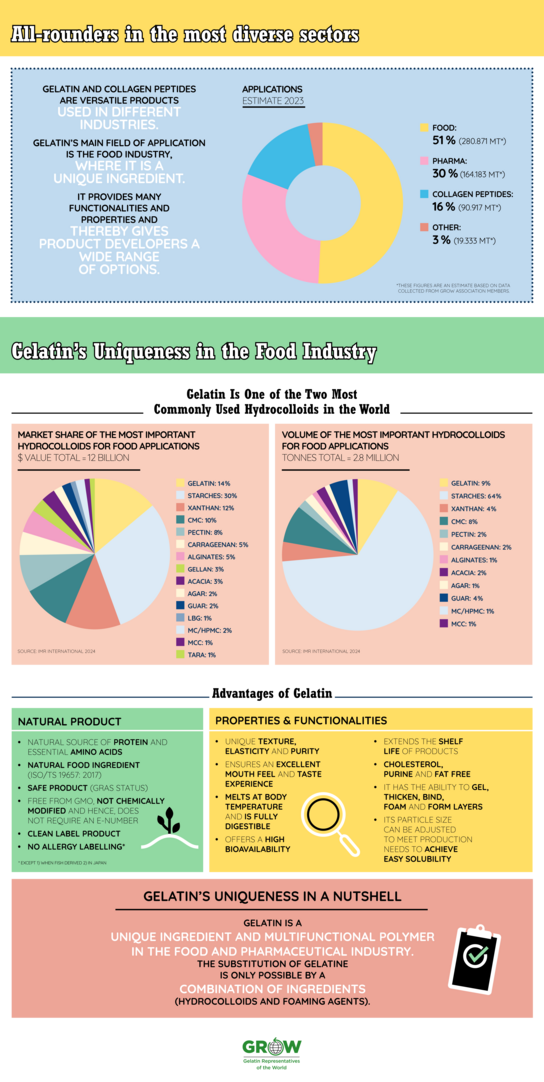
The most common usage of gelatin is edible gelatin followed by pharmaceutical, photographic and technical gelatin. What makes gelatin so unique is its remarkable number of functional properties. These include the ability to gel, thicken, stabilize, foam or bind water. In addition, gelatin is 100 per cent natural and is cholesterol, purine and fat free. It does not contain any substances listed as allergen in official regulations. Another reason for being an ideal clean label ingredient.
There is no other natural ingredient in the world that combines all of the above-mentioned and necessary properties in just one food product. Many applications need several of gelatin’s properties to be able to manufacture the final product. Only a combination of various ingredients would even come close to gelatin’s properties.
A range of gelatins can be manufactured depending upon the type of application or customer requirements. There are countless types of gelatin that are distinguished based on several factors. One of the most important is the Bloom value – it defines gelatin’s ability to gelatinize. The vast majority of gelatin is produced in the form of a white, odorless and tasteless powder.
Natural
As a natural food, gelatin is thus a valuable source of protein for the human organism. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. The human body is able to synthesize all the proteins it needs from amino acids. There are, however, nine amino acids that the body cannot produce by itself and which must therefore be ingested regularly through the diet. They are called the essential amino acids. Gelatin contains a total of 18 amino acids, including eight of the nine essential amino acids.
Two forms of gelatin
Leaf gelatin
One special form of gelatin is leaf gelatin. It is used in the household, in cooking, in bakeries, confectionery shops and butcher’s shops, in catering and for other non-industrial applications. The gelatin is cut into squares and has a netlike pattern that is a result of the production process. At first glance, this and the elasticity of the sheets make leaf gelatin look more like an artwork. The great advantage of leaf gelatin is that it can easily be divided into portions according to recipe instructions and is thus easy to use during cooking.
Instant gelatin
Instant gelatin can be directly processed under cold conditions and is specially developed for final products that are temperature sensitive and should not be heated. Instant gelatin is often used to stabilize foods such as cakes, desserts and other sweet and cold dishes.
The all-rounder at a glance
Discover more!
Learn more about some of gelatin’s unique properties and advantages by watching the video series on GROW’s blog