General Information about Hydrocolloids
The term hydrocolloid encompasses a large group of polysaccharides and proteins that go into solution in water as colloids and demonstrate a high propensity for forming gels.
Gelatin contains all these characteristics and has the widest range of functionalities. It has been consumed for more than 2,000 years and known for generations. So people often prefer gelatin to relatively recently developed hydrocolloids.

Functionalities
They are part of our everyday life and bring added value to many products thanks to their various technical functionalities, such as:
- Texturing
- Thickening
- (Water)-binding
- Emulsifying
- Stabilizing
- Foaming
- Film forming
- Gelling
- Fining
- Adhesion
Properties
In addition, these unique properties make it a key ingredient:
- Thermo-reversible gel formation
- Transparency
- Natural protein
- Melting at body temperature
The Numerous Advantages of Using Gelatin
The undeniable benefits of using gelatin as an ingredient of choice can be divided as follows:
Gelatine is...
… a clean label product
- is a natural food ingredient with no e-number
- is a clean label and does not require any chemical modification
- is a natural protein containing a total of 18 amino acids, including eight of the nine essential amino acids (can’t be produced by the human body)
- is considered a natural ingredient in accordance with the ISO technical specification on definitions and technical criteria (ISO/TS 19657:2017)
- consistency and purity are natural properties of gelatin
- has GRAS status (Generally Recognized As Safe): gelatin is a completely safe product
- can be declared GMO-free
- is cholesterol-, purine- and fat-free
- gels within the normal pH range of most foodstuffs and does not require the addition of salts, sugar or acids to gel
… easy to digest
- is complete and easy to digest with a high bioavailability
- can be consumed daily without reservations
- know-how about gelatin and its metabolism has been developed over many years
- forms a thermo-reversible gel that melts at body temperature
… has a longer shelf life
- ensures longer shelf life and stabilizes delicate food products for easier transport and storage
- The quantities of substitute required will increase compared to gelatin. As a consequence, the mouthfeel will change
... can be applied in various fields
- is versatile in its applications: gels, thickens, binds with water, emulsifies, foams, forms layers
- can only be substituted by a combination of ingredients (hydrocolloids, foaming agents, etc.) as gelatin is a unique multifunctional polymer
- the wide variety of gelatin enables to meet the individual application specifications
- diverse in texture
- is available in various gel strengths and grain sizes
- particle size can be adjusted to meet production needs and achieve easy solubility
- ensures an excellent mouth feel and an intense taste experience
That is why gelatin has an unmatched profile
Gelatin is a versatile product that is commonly used in different industries. Its main field of application is the food industry. Click here to learn more about all fields of application.
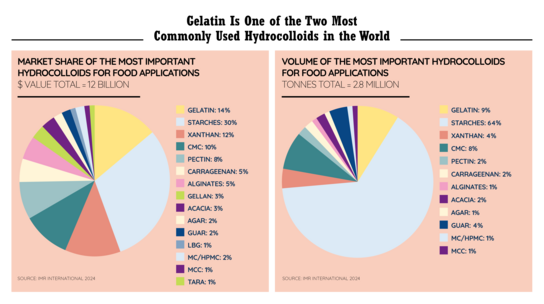
Overview: Hydrocolloids in the Food Industry
Gelatin is one of the two most commonly used hydrocolloids in the world. Others are acacia, agar, alginates, carrageenan, cellulosics (CMC, MCC, MC/HPMC), gellan, guar, locust bean gum (LBG), pectin, starch, tara gum, and xanthan.